|
A · B · C · D · E · F · G · H · I · J · K · L · M · N · O · P · Q · R · S · T · U · V · W · X · Y · Z
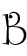
bacteria
A group of unicellular microorganisms lacking chlorophyll and reproducing rapidly by simple fission. Are known to be responsible for the spoilage and contamination of beer. There are no known pathogenic bacteria that can grow in beer.
bacteriostatic
Bacteria inhibiting.
°balling
A standard European measurement of the density of solutions, calibrated on the weight of cane sugar in solution. Measured in degrees.
barley
A cereal of the genus Hordeum, a member of the Gramineae or grass family of plants that also includes wheat, rye, oats, maize, rice, millet and sorghum. There are two varieties (2-row, 6-row) classified according to the number of rows of seeds on each of the heads of the plant. When malted, barley is the cereal grain preferred for brewing because the seed is covered by a husk that protects the germ during malting and helps to filter the wort during lautering by forming a filter bed. The essential qualities for brewing barley are high starch content, sufficient diastatic power to transform the starch into sugar, and low protein content.
barleycorn
Seed of the barley plant.
barley malt
Processed barley. See barley and malt.
barrel
Standard unit in commercial brewing. U.S. barrel is 31.5 gallons; British barrel is 43.2 U.S. gallons. Abbreviation; bbl.
beta-amylase
An enzyme that bleaks down starches into smaller chains by chopping off maltose molecules from the end. This process is called saccharification because it produces fermentable sugars. Beta-amylase is most active at temperatures between 113-149 °F (45-65 °C).
beerstone
Brownish-gray, calcium oxalate and organic deposits left on fermentation equipment.
beer
Generic term that describes any fermented beverage made from barley malt or other cereal grains. Originally denoted products containing hops instead of other herbs. From the latin bibere meaning to drink
beta glucans
A group of gummy carbohydrates in malt. Some varieties can cause problems with runoff, and during fermentation.
bitterness
A desirable flavor quality created by the isohumulones of hops. See HBU and IBM.
bitter flavor
Basic taste associated with hops; braun-hefe or malt husks. Sensation experienced on the back of the tongue.
body
A quality of beer, largely determined by the presence of colloidal protein complexes. Also partially due to the presence of unfermentable sugars (dextrins) in the finished beer.
bottle-capper
A device used for capping (sealing) beer bottles, usually with crown seals.
braggot
Meads made with both honey and malt providing flavor and fermentable extract. Originally, and alternatively, a mixture of mead and ale.
break
The sudden precipitation of proteins and resins in wort. The hot break occurs during the boil, and the cold break occurs during rapid chilling.
brew
To make beer.
brewer
A person who makes beer. From the Gallic word brai (or brace) originally meaning barley, and later barley mixed with water.
buffer
A substance capable of resisting changes in the pH of a solution.
bung
Wooden plug for beer barrel or cask.
burton salts
Mixture of minerals added to brewing water to approximate the water of Burton-on-Trent, England, famous for the production of pale ales.
buttery flavor
Described as buttery or butterscotch. Sometimes caused by abbreviated fermentation, mutated yeast or bacteria. Also known as diacetyl flavor.
|